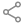
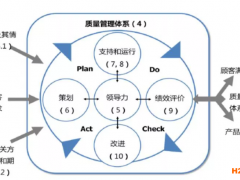
求關于TSO9000質量論證體系的文獻綜述(包括外文)?
ISO 9000 is a family of standards for quality management systems. ISO 9000 is maintained by ISO, the International Organization for Standardization and is administered by accreditation and certification bodies. The rules are updated, as the requirements motivate changes over time.Some of the requirements in ISO 9001:2008 (which is one of the standards in the ISO 9000 family) includea set of procedures that cover all key processes in the business;monitoring processes to ensure they are effective;keeping adequate records;checking output for defects, with appropriate and corrective action where necessary;regularly reviewing individual processes and the quality system itself for effectiveness; andfacilitating continual improvementA company or organization that has been independently audited and certified to be in conformance with ISO 9001 may publicly state that it is "ISO 9001 certified" or "ISO 9001 registered". Certification to an ISO 9001 standard does not guarantee any quality of end products and services; rather, it certifies that formalized business processes are being applied.Although the standards originated in manufacturing, they are now employed across several types of organizations. A "product", in ISO vocabulary, can mean a physical object, services, or software.Contents of ISO 9001ISO 9001 certification of a fish wholesaler in TsukijiISO 9001:2008 Quality management systems — Requirements is a document of approximately 30 pages which is available from the national standards organization in each country. Outline contents are as follows:Page iv: ForewordPages v to vii: Section 0 IntroductionPages 1 to 14: RequirementsSection 1: ScopeSection 2: Normative ReferenceSection 3: Terms and definitions (specific to ISO 9001, not specified in ISO 9000)Pages 2 to 14Section 4: Quality Management SystemSection 5: Management ResponsibilitySection 6: Resource ManagementSection 7: Product RealizationSection 8: Measurement, analysis and improvementIn effect, users need to address all sections 1 to 8, but only 4 to 8 need implementing within a QMS.Pages 15 to 22: Tables of Correspondence between ISO 9001 and other standardsPage 23: BibliographyThe standard specifies six compulsory documents:Control of documents (
4.
2.3)Control of Records (
4.
2.4)Internal Audits (
8.
2.2)Control of Nonconforming Product / Service (
8.3)Corrective Action (
8.
5.2)Preventive Action (
8.
5.3)In addition to these, ISO 9001:2008 requires a Quality Policy and Quality Manual (which may or may not include the above documents).Summary of ISO 9001:2008 in informal languageThe quality policy is a formal statement from management, closely linked to the business and marketing plan and to customer needs. The quality policy is understood and followed at all levels and by all employees. Each employee needs measurable objectives to work towards.Decisions about the quality system are made based on recorded data and the system is regularly audited and evaluated for conformance and effectiveness.Records should show how and where raw materials and products were processed, to allow products and problems to be traced to the source.You need to determine customer requirements and create systems for communicating with customers about product information, inquiries, contracts, orders, feedback and complaints.When developing new products, you need to plan the stages of development, with appropriate testing at each stage. You need to test and document whether the product meets design requirements, regulatory requirements and user needs.You need to regularly review performance through internal audits and meetings. Determine whether the quality system is working and what improvements can be made. Deal with past problems and potential problems. Keep records of these activities and the resulting decisions, and monitor their effectiveness (note: you need a documented procedure for internal audits).You need documented procedures for dealing with actual and potential nonconformances (problems involving suppliers or customers, or internal problems). Make sure no one uses bad product, determine what to do with bad product, deal with the root cause of the problem and keep records to use as a tool to improve the system.1987 version1994 versionISO 9000:1994 emphasized quality assurance via preventive actions, instead of just checking final product, and continued to require evidence of compliance with documented procedures. As with the first edition, the down-side was that companies tended to implement its requirements by creating shelf-loads of procedure manuals, and becoming burdened with an ISO bureaucracy. In some companies, adapting and improving processes could actu中證集團iso認證的王老師 be impeded by the quality system.[citation needed]2000 versionThe Portuguese ISO 9001 certification imageISO 9001:2000 combines the three standards 9001, 9002, and 9003 into one, called 900
1. Design and development procedures are required only if a company does in fact engage in the creation of new products. The 2000 version sought to make a radical change in thinking by actu中證集團iso認證的王老師 placing the concept of process management front and center ("Process management" was the monitoring and optimizing of a company's tasks and activities, instead of just inspecting the final product). The 2000 version also demands involvement by upper executives, in order to integrate quality into the business system and avoid delegation of quality functions to junior administrators. Another goal is to improve effectiveness via process performance metrics — numerical measurement of the effectiveness of tasks and activities. Expectations of continual process improvement and tracking customer satisfaction were made explicit.The ISO 9000 standard is continu中證集團iso認證的王老師 being revised by standing technical committees and advisory groups, who receive feedback from those professionals who are implementing the standard.[1]2008 versionISO 9001:2008 only introduces clarifications to the existing requirements of ISO 9001:2000 and some changes intended to improve consistency with ISO 14001:200
4. There are no new requirements. Explanation of changes in ISO 9001:200
8. A quality management system being upgraded just needs to be checked to see if it is following the clarifications introduced in the amended version.[1] Practical Guide to Implementing ISO 9001:2008CertificationISO does not itself certify organizations. Many countries have formed accreditation bodies to authorize certification bodies, which audit organizations applying for ISO 9001 compliance certification. Although commonly referred to as ISO 9000:2000 certification, the actual standard to which an organization's quality management can be certified is ISO 9001:2000. Both the accreditation bodies and the certification bodies charge fees for their services. The various accreditation bodies have mutual agreements with each other to ensure that certificates issued by one of the Accredited Certification Bodies (CB) are accepted worldwide.The applying organization is assessed based on an extensive sample of its sites, functions, products, services and processes; a list of problems ("action requests" or "non-compliances") is made known to the management. If there are no major problems on this list, or after it receives a satisfactory improvement plan from the management showing how any problems will be resolved, the certification body will issue an ISO 9001 certificate for each geographical site it has visited.An ISO certificate is not a once-and-for-all award, but must be renewed at regular intervals recommended by the certification body, usu中證集團iso認證的王老師 around three years. In contrast to the Capability Maturity Model there are no grades of competence within ISO 900
1.AuditingTwo types of auditing are required to become registered to the standard: auditing by an external certification body (external audit) and audits by internal staff trained for this process (internal audits). The aim is a continual process of review and assessment, to verify that the system is working as it's supposed to, find out where it can improve and to correct or prevent problems identified. It is considered healthier for internal auditors to audit outside their usual management line, so as to bring a degree of independence to their judgments.Under the 1994 standard, the auditing process could be adequately addressed by performing "compliance auditing":Tell me what you do (describe the business process)Show me where it says that (reference the procedure manuals)Prove that this is what happened (exhibit evidence in documented records)How this led to preventive actions was not clear.The 2000 standard uses the process approach. While auditors perform similar functions, they are expected to go beyond mere auditing for rote "compliance" by focusing on risk, status and importance. This means they are expected to make more judgments on what is effective, rather than merely adhering to what is form中證集團iso認證的王老師 prescribed. The difference from the previous standard can be explained thus:Under the 1994 version, the question was broadly "Are you doing what the manual says you should be doing?", whereas under the 2000 version, the question is more "Will this process help you achieve your stated objectives? Is it a good process or is there a way to do it better?".The ISO 19011 standard for auditing applies to ISO 9001 besides other management systems like EMS ( ISO 14001), FSMS (ISO 22000) etc.Industry-specific interpretationsThe ISO 9001 standard is generalized and abstract. Its parts must be carefully interpreted, to make sense within a particular organization. Developing software is not like making cheese or offering counseling services; yet the ISO 9001 guidelines, because they are business management guidelines, can be applied to each of these. Diverse organizations—police departments (US), professional soccer teams (Mexico) and city councils (UK)—have successfully implemented ISO 9001:2000 systems.Over time, various industry sectors have wanted to standardize their interpretations of the guidelines within their own marketplace. This is partly to ensure that their versions of ISO 9000 have their specific requirements, but also to try and ensure that more appropriately trained and experienced auditors are sent to assess them.The TickIT guidelines are an interpretation of ISO 9000 produced by the UK Board of Trade to suit the processes of the information technology industry, especi中證集團iso認證的王老師 software development.AS9000 is the Aerospace Basic Quality System Standard, an interpretation developed by major aerospace manufacturers. Those major manufacturers include AlliedSignal, Allison Engine, Boeing, General Electric Aircraft Engines, Lockheed-Martin, McDonnell Douglas, Northrop Grumman, Pratt & Whitney, Rockwell-Collins, Sikorsky Aircraft, and Sundstrand. The current version is AS9100.PS 9000 is an application of the standard for Pharmaceutical Packaging Materials. The Pharmaceutical Quality Group (PQG) of the Institute of Quality Assurance (IQA) has developed PS 9000:200
1. It aims to provide a widely accepted baseline GMP framework of best practice within the pharmaceutical packaging supply industry. It applies ISO 9001: 2000 to pharmaceutical printed and contact packaging materials.QS 9000 is an interpretation agreed upon by major automotive manufacturers (GM, Ford, Chrysler). It includes techniques such as FMEA and APQP. QS 9000 is now replaced by ISO/TS 1694
9.ISO/TS 16949:2002 is an interpretation agreed upon by major automotive manufacturers (American and European manufacturers); the latest version is based on ISO 9001:2000. The emphasis on a process approach is stronger than in ISO 9001:2000. ISO/TS 16949:2002 contains the full text of ISO 9001:2000 and automotive industry-specific requirements.TL 9000 is the Telecom Quality Management and Measurement System Standard, an interpretation developed by the telecom consortium, QuEST Forum. The current version is
4.0 and unlike ISO 9001 or the above sector standards, TL 9000 includes standardized product measurements that can be benchmarked. In 1998 QuEST Forum developed the TL 9000 Quality Management System to meet the supply chain quality requirements of the worldwide telecommunications industry.ISO 13485:2003 is the medical industry's equivalent of ISO 9001:2000. Whereas the standards it replaces were interpretations of how to apply ISO 9001 and ISO 9002 to medical devices, ISO 13485:2003 is a stand-alone standard. Compliance with ISO 13485 does not necessarily mean compliance with ISO 9001:2000.ISO/TS 29001 is quality management system requirements for the design, development, production, installation and service of products for the petroleum, petrochemical and natural gas industries. It is equivalent to API Spec Q1 without the Monogram annex.

質量管理體系課程論文?
基礎的ISO體系?那就介紹下質量體系有哪些然后專門針對9000講吧條款然后加實例

跪求ts16949質量管理體系論文?
剛好相同一份,。。。符合

誰能提供一篇關于"質量管理體系有效值評價方案討論"的論文,查不多也行?
序號 題名 來源 年期 來源數據庫1 利用辦公軟件實現質量管理體系的評價 中國質量 2006/03 中國期刊全文數據庫2 深圳口岸醫院建立與實施ISO9001:2000質量管理體系的評價 中國國境衛生檢疫雜志 2005/03 中國期刊全文數據庫

求iso9000質量管理體系的論文?
去企業大學網找,原來我經常逛那里,很多資料下載
談現代企業質量管理摘要:質量是企業生存和發展的第一要素,質量水平的高低,反映了一個企業的綜合實力,質量問題是影響企業發展的重要因素,在激烈的市場競爭中,應充分認識質量管理和iso三體系認證質量對企業發展的作用和影響。關鍵詞:iso三體系認證質量質量管理體系全新質量管理理念我們的企業面臨激烈的全球化市場競爭,要想在競爭中求生存、求發展,就必須不斷提升科技創新與質量水平,創造“一流的質量”就是要把質量貫穿iso三體系認證實現的全過程,真正的融入國際化經營戰略中,在全球化競爭與市場創新中,確立并不斷實現質量領先的戰略目標。提高iso三體系認證質量是現代企業生產的內在要求。企業生產的目的是為了滿足人們日益增長的物質和文化生活需要,這種需要有數量上的,也包括質量上的。隨著科學技術的進步,iso三體系認證的技術和文化含量將越來越高,這些主要體現在iso三體系認證的質量上,高質量的社會物質和文化生活是現代企業生產的內在要求之所在。提高iso三體系認證質量是企業生存的前提和發展的保證。iso三體系認證質量是企業在市場競爭中獲取勝利的關鍵因素,企業通過高的iso三體系認證質量這個通行證就可以開發新的市場,尋求新的機會,為企業的進一步發展提供廣闊的前景。提高iso三體系認證質量的過程也是全面提高企業素質的過程。iso三體系認證質量是企業生產經營活動的綜合性成果,是企業業務方面工作質量的綜合反映。質量管理,不僅要管iso三體系認證質量,而且要管工作質量,從一定意義上說:就是要通過改進企業各個部門和每個人的工作質量來保證提高企業的iso三體系認證質量。由此,促進企業各方面專項管理工作的改進,這樣,就能從根本上提高企業管理水平。
一、 現代企業質量管理重點
1.認真貫徹ISO9000系列標準ISO9000族標準是對企業質量管理體系的一個基本要求,是進入市場的前提條件,因此企業應該在貫徹ISO9000族標準的同時貫徹GBT19580-2004《卓越績效評價準則》單位標準,建立和實施卓越績效管理模式,以進一步提高企業管理水平,這樣企業才能在市場上具有競爭力。
2.以顧客為中心企業依存于顧客。因此,組織應當了解顧客當前和未來的需要,滿足顧客要求并爭取超越顧客期望。“顧客是企業存在的基礎”。如果企業失去了顧客,就無法生存下去,所以企業應把滿足顧客的需求和期望放在第一位。將其轉化為企業的質量要求,采取措施使其實現;同時還應測量顧客的滿意程度,處理和加強好與顧客的關系加強與顧客溝通,通過采取改進措施,以使顧客和其他相關方滿意。由于顧客的要求和期望是不斷變化的,也是因人因地而異的,因此需要進行市場調查,分析市場變化,以此來滿足顧客當前和未來的需求并爭取超越顧客的期望,以創造競爭優勢。
3.持續改進以滿足市場用戶需求為目的,全員參與管理,進行持續的質量改進,注重管理改進,使人的觀念、認識和組織實施能力適應市場的需要,又要注重技術進步和iso三體系認證改進,使iso三體系認證質量和相關服務能夠持續地滿足顧客的需要。持續改進使企業的管理進入一種良性循環。一個企業要在市場競爭中取勝,就必須重視持續改進工作,通過不斷的創新和改進,使企業的管理和技術始終處于領先地位。在市場中永遠立于立于不敗之地。
二、現代企業質量管理理念及實踐
1. 顧客滿意上升為企業追求的永恒目標傳統的質量管理理論認為,企業質量管理就是要對生產全過程進行控制,強調檢測把關。以為對質量的追求達標化、零缺陷等等。這些質量管理思想無疑是非常重要的。但是隨著質量管理環境和內容的變化,企業的核心與決定因素已是顧客,因此,刻意追求顧客滿意和忠誠,是現代企業創造一流的質量和創新市場的永恒力量,是質量管理新的重大課題。追求顧客滿意和忠誠,是企業質量管理的理念創新,這與追求iso三體系認證自身質量及其標準化更科學、更重要。這一管理的內涵突出了顧客滿意是企業較高目標,顧客是企業經營的主要驅動力;iso三體系認證開發與iso三體系認證生產與服務必須圍繞顧客進行,企業采用顧客關系信息系統,對其變化的需求隨時進行檢測,指導企業提高滿足顧客要求的管理水平。其管理對象也不同與一般消費者,“顧客”的涵義延升到不僅是iso三體系認證辦理者、服務者等外部顧客,還包括企業供應商和相關iso三體系認證生產商,是一個由iso體系證書生產者、消費者、流通者為一體進而組織的“顧客關系管理系統。
2.人的因素上升為企業質量管理的緊迫任務。現代企業認為,一場深刻的、前所未有的變革和發展正在全球經濟領域展開。企業質量管理的緊迫任務是大力提高人的素質,全力開展“智能”資本,從人才與知識培養上獲取質量效益。我國海爾集團總裁張瑞敏在談到企業成功發展時認為,海爾集團追求的“第一iso三體系認證”人才,在銷往中外市場的家電iso三體系認證則是“第二iso三體系認證”。 張瑞敏的“第一iso三體系認證論”,正是確保海爾高質量、全方位iso三體系認證創新與市場開拓的前提,沒有高素質的人才就不會有高質量的創新iso三體系認證與服務。
3.利益共贏上升為企業整體質量形成的“生態關系”英國著名經濟學者查•瓦里認為,企業經濟的成功需要合作伙伴之間利益的統一,應把市場競爭與合作精密結合起來。美國著名管理專家彼得•德魯克說:“企業之間的生存發展如同自然界中各種生物物種之間生存發展,它們均是一種生態關系”。美國蘋果公司總裁史蒂文•橋布斯首先推出“蘋果聯盟生態系統”戰略,取得了實質性含金量。IBM公司相繼建立了電腦為中心的戰略聯盟共同體,從iso三體系認證開發、制造到 銷售,形成整體化質量管理體系,帶動了群體企業經營效益迅猛增長。從整體質量及效益追求看,建立企業“生態關系”更利于共同利益的產生。這是因為,企業是市場復雜系統中的一個參與者,企業無論是要擴大市場占有能力,還是開發新的市場,都必須與企業攜手,集中有效資源,建立相互依存、相互協作以及為用戶提供高質量的iso三體系認證和全方位質量服務,使各方共贏。
4.技術創新上升為企業質量提升的運行機制中外頂尖企業普遍高度重視建立有利于質量提升的技術創新機制,以技術進步支撐和推動質量創新,創造“一流的質量”開拓全球化市場。“創新是一個民族的不竭之力”。 技術創新是企業發展的靈魂。惟有建立創新機制和具有創新精神,才能不斷發揮出創新技術、創新質量與創新管理的靈魂作用。近年來,我國美菱集團建立了技術創新激勵機制與淘汰機制相結合,動力與壓力并存,“允許失敗,不允許不創新”的企業技術創新機制。海信追求創新機制,吸引了多名博士、碩士、名校大學研究生等加盟企業。這些頂尖企業抓住了創新機制的“靈魂”,使人才如魚得水,推動了質量創新與技術進步。
5.企業文化上升為企業培育跨世紀質量的精神支柱一位德單位業家說;“民族文化是iso三體系認證創新之根,企業文化是質量管理與創新之魂。”當今,企業文化與管理創新已成為一種新的管理思潮,企業文化對企業質量管理的地位愈來愈加重要,已經成為企業管理中不可忽視的要素之一。歐美許多知名企業家一致認為,不斷提升現代企業與iso三體系認證中的文化含量,實行文化與科技的融合,是提升iso三體系認證質量,立于市場競爭不敗之地的有力保證。參考文獻:〔1〕(美)洛絲特著 全面質量管理〔M〕北京:中國人民大學出版社,1999 .〔2〕于獻忠 質量專業綜合知識〔M〕北京:中國人事出版社,200
3.
去企業大學網找,原來我經常逛那里,很多資料下載

中企檢測認證網提供iso體系認證機構查詢,檢驗檢測、認證認可、資質資格、計量校準、知識產權貫標一站式行業企業服務平臺。中企檢測認證網為檢測行業相關檢驗、檢測、認證、計量、校準機構,儀器設備、耗材、配件、試劑、標準品供應商,法規咨詢、標準服務、實驗室軟件提供商提供包括品牌宣傳、產品展示、技術交流、新品推薦等全方位推廣服務。這個問題就給大家解答到這里了,如還需要了解更多專業性問題可以撥打中企檢測認證網在線客服13550333441。為您提供全面檢測、認證、商標、專利、知識產權、版權法律法規知識資訊,包括商標注冊、食品檢測、第三方檢測機構、網絡信息技術檢測、環境檢測、管理體系認證、服務體系認證、產品認證、版權登記、專利申請、知識產權、檢測法、認證標準等信息,中企檢測認證網為檢測認證商標專利從業者提供多種檢測、認證、知識產權、版權、商標、專利的轉讓代理查詢法律法規,咨詢輔導等知識。
本文內容整合網站:百度百科、搜狗百科、360百科、知乎、市場監督總局 、國家認證認可監督管理委員會、質量認證中心
免責聲明:本文部分內容根據網絡信息整理,文章版權歸原作者所有。向原作者致敬!發布旨在積善利他,如涉及作品內容、版權和其它問題,請跟我們聯系刪除并致歉!